mirror of
https://github.com/S2-/minifyfromhtml.git
synced 2025-08-03 12:20:04 +02:00
update packages to latest version
This commit is contained in:
146
node_modules/decimal.js/README.md
generated
vendored
146
node_modules/decimal.js/README.md
generated
vendored
@@ -18,7 +18,8 @@ An arbitrary-precision Decimal type for JavaScript.
|
||||
- Faster, smaller, and perhaps easier to use than JavaScript versions of Java's BigDecimal
|
||||
- No dependencies
|
||||
- Wide platform compatibility: uses JavaScript 1.5 (ECMAScript 3) features only
|
||||
- Comprehensive [documentation](http://mikemcl.github.io/decimal.js/) and test set
|
||||
- Comprehensive [documentation](https://mikemcl.github.io/decimal.js/) and test set
|
||||
- Used under the hood by [math.js](https://github.com/josdejong/mathjs)
|
||||
- Includes a TypeScript declaration file: *decimal.d.ts*
|
||||
|
||||
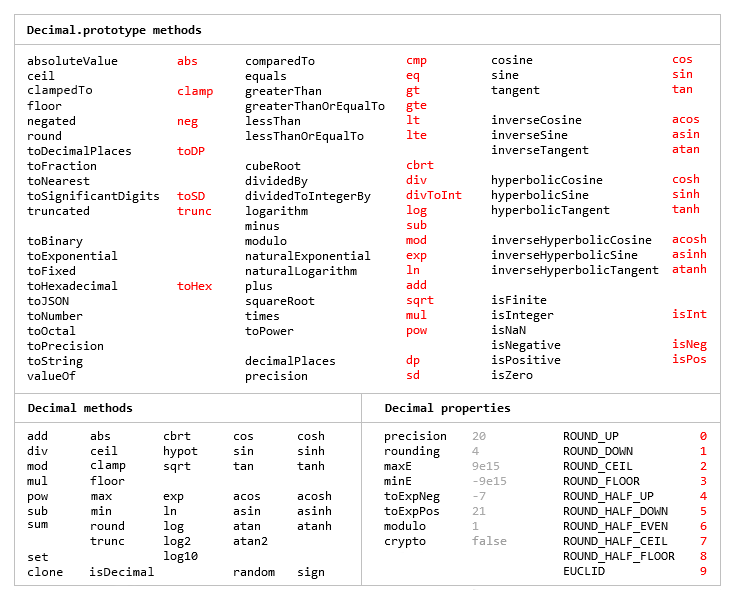
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +33,8 @@ This library also adds the trigonometric functions, among others, and supports n
|
||||
which makes it a significantly larger library than *bignumber.js* and the even smaller
|
||||
[big.js](https://github.com/MikeMcl/big.js/).
|
||||
|
||||
For a lighter version of this library without the trigonometric functions see [decimal.js-light](https://github.com/MikeMcl/decimal.js-light/).
|
||||
For a lighter version of this library without the trigonometric functions see
|
||||
[decimal.js-light](https://github.com/MikeMcl/decimal.js-light/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Load
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -42,48 +44,32 @@ Browser:
|
||||
|
||||
```html
|
||||
<script src='path/to/decimal.js'></script>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```html
|
||||
<script type="module">
|
||||
import Decimal from './path/to/decimal.mjs';
|
||||
...
|
||||
import Decimal from './path/to/decimal.mjs';
|
||||
...
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[Node.js](http://nodejs.org):
|
||||
[Node.js](https://nodejs.org):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ npm install decimal.js
|
||||
npm install decimal.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
var Decimal = require('decimal.js');
|
||||
```
|
||||
const Decimal = require('decimal.js');
|
||||
|
||||
ES module:
|
||||
import Decimal from 'decimal.js';
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
//import Decimal from 'decimal.js';
|
||||
import {Decimal} from 'decimal.js';
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
AMD loader libraries such as [requireJS](http://requirejs.org/):
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
require(['decimal'], function(Decimal) {
|
||||
// Use Decimal here in local scope. No global Decimal.
|
||||
});
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Use
|
||||
|
||||
*In all examples below, `var`, semicolons and `toString` calls are not shown.
|
||||
*In all examples below, semicolons and `toString` calls are not shown.
|
||||
If a commented-out value is in quotes it means `toString` has been called on the preceding expression.*
|
||||
|
||||
The library exports a single function object, `Decimal`, the constructor of Decimal instances.
|
||||
|
||||
It accepts a value of type number, string or Decimal.
|
||||
The library exports a single constructor function, `Decimal`, which expects a single argument that is a number, string or Decimal instance.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
x = new Decimal(123.4567)
|
||||
@@ -92,7 +78,29 @@ z = new Decimal(x)
|
||||
x.equals(y) && y.equals(z) && x.equals(z) // true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A value can also be in binary, hexadecimal or octal if the appropriate prefix is included.
|
||||
If using values with more than a few digits, it is recommended to pass strings rather than numbers to avoid a potential loss of precision.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Precision loss from using numeric literals with more than 15 significant digits.
|
||||
new Decimal(1.0000000000000001) // '1'
|
||||
new Decimal(88259496234518.57) // '88259496234518.56'
|
||||
new Decimal(99999999999999999999) // '100000000000000000000'
|
||||
|
||||
// Precision loss from using numeric literals outside the range of Number values.
|
||||
new Decimal(2e+308) // 'Infinity'
|
||||
new Decimal(1e-324) // '0'
|
||||
|
||||
// Precision loss from the unexpected result of arithmetic with Number values.
|
||||
new Decimal(0.7 + 0.1) // '0.7999999999999999'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As with JavaScript numbers, strings can contain underscores as separators to improve readability.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
x = new Decimal('2_147_483_647')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
String values in binary, hexadecimal or octal notation are also accepted if the appropriate prefix is included.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
x = new Decimal('0xff.f') // '255.9375'
|
||||
@@ -101,15 +109,13 @@ z = x.plus(y) // '427.9375'
|
||||
|
||||
z.toBinary() // '0b110101011.1111'
|
||||
z.toBinary(13) // '0b1.101010111111p+8'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Using binary exponential notation to create a Decimal with the value of `Number.MAX_VALUE`:
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Using binary exponential notation to create a Decimal with the value of `Number.MAX_VALUE`.
|
||||
x = new Decimal('0b1.1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111p+1023')
|
||||
// '1.7976931348623157081e+308'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A Decimal is immutable in the sense that it is not changed by its methods.
|
||||
Decimal instances are immutable in the sense that they are not changed by their methods.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
0.3 - 0.1 // 0.19999999999999998
|
||||
@@ -128,27 +134,28 @@ x.times('1.23456780123456789e+9').plus(9876.5432321).dividedBy('4444562598.11177
|
||||
Many method names have a shorter alias.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
x.squareRoot().dividedBy(y).toPower(3).equals(x.sqrt().div(y).pow(3)) // true
|
||||
x.cmp(y.mod(z).neg()) == 1 && x.comparedTo(y.modulo(z).negated()) == 1 // true
|
||||
x.squareRoot().dividedBy(y).toPower(3).equals(x.sqrt().div(y).pow(3)) // true
|
||||
x.comparedTo(y.modulo(z).negated() === x.cmp(y.mod(z).neg()) // true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Like JavaScript's Number type, there are `toExponential`, `toFixed` and `toPrecision` methods,
|
||||
Most of the methods of JavaScript's `Number.prototype` and `Math` objects are replicated.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
x = new Decimal(255.5)
|
||||
x.toExponential(5) // '2.55500e+2'
|
||||
x.toFixed(5) // '255.50000'
|
||||
x.toPrecision(5) // '255.50'
|
||||
```
|
||||
x.toExponential(5) // '2.55500e+2'
|
||||
x.toFixed(5) // '255.50000'
|
||||
x.toPrecision(5) // '255.50'
|
||||
|
||||
and almost all of the methods of JavaScript's Math object are also replicated.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
Decimal.sqrt('6.98372465832e+9823') // '8.3568682281821340204e+4911'
|
||||
Decimal.pow(2, 0.0979843) // '1.0702770511687781839'
|
||||
|
||||
// Using `toFixed()` to avoid exponential notation:
|
||||
x = new Decimal('0.0000001')
|
||||
x.toString() // '1e-7'
|
||||
x.toFixed() // '0.0000001'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are `isNaN` and `isFinite` methods, as `NaN` and `Infinity` are valid `Decimal` values,
|
||||
And there are `isNaN` and `isFinite` methods, as `NaN` and `Infinity` are valid `Decimal` values.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
x = new Decimal(NaN) // 'NaN'
|
||||
@@ -156,7 +163,7 @@ y = new Decimal(Infinity) // 'Infinity'
|
||||
x.isNaN() && !y.isNaN() && !x.isFinite() && !y.isFinite() // true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and a `toFraction` method with an optional *maximum denominator* argument
|
||||
There is also a `toFraction` method with an optional *maximum denominator* argument.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
z = new Decimal(355)
|
||||
@@ -165,27 +172,27 @@ pi.toFraction() // [ '7853982301', '2500000000' ]
|
||||
pi.toFraction(1000) // [ '355', '113' ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
All calculations are rounded according to the number of significant digits and rounding mode
|
||||
specified by the `precision` and `rounding` properties of the Decimal constructor.
|
||||
All calculations are rounded according to the number of significant digits and rounding mode specified
|
||||
by the `precision` and `rounding` properties of the Decimal constructor.
|
||||
|
||||
For advanced usage, multiple Decimal constructors can be created, each with their own independent configuration which
|
||||
applies to all Decimal numbers created from it.
|
||||
For advanced usage, multiple Decimal constructors can be created, each with their own independent
|
||||
configuration which applies to all Decimal numbers created from it.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
// Set the precision and rounding of the default Decimal constructor
|
||||
Decimal.set({ precision: 5, rounding: 4 })
|
||||
|
||||
// Create another Decimal constructor, optionally passing in a configuration object
|
||||
Decimal9 = Decimal.clone({ precision: 9, rounding: 1 })
|
||||
Dec = Decimal.clone({ precision: 9, rounding: 1 })
|
||||
|
||||
x = new Decimal(5)
|
||||
y = new Decimal9(5)
|
||||
y = new Dec(5)
|
||||
|
||||
x.div(3) // '1.6667'
|
||||
y.div(3) // '1.66666666'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The value of a Decimal is stored in a floating point format in terms of its digits, exponent and sign.
|
||||
The value of a Decimal is stored in a floating point format in terms of its digits, exponent and sign, but these properties should be considered read-only.
|
||||
|
||||
```js
|
||||
x = new Decimal(-12345.67);
|
||||
@@ -198,47 +205,42 @@ For further information see the [API](http://mikemcl.github.io/decimal.js/) refe
|
||||
|
||||
## Test
|
||||
|
||||
The library can be tested using Node.js or a browser.
|
||||
|
||||
The *test* directory contains the file *test.js* which runs all the tests when executed by Node,
|
||||
and the file *test.html* which runs all the tests when opened in a browser.
|
||||
|
||||
To run all the tests, from a command-line at the root directory using npm
|
||||
To run the tests using Node.js from the root directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ npm test
|
||||
npm test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or at the *test* directory using Node
|
||||
Each separate test module can also be executed individually, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ node test
|
||||
node test/modules/toFraction
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Each separate test module can also be executed individually, for example, at the *test/modules* directory
|
||||
To run the tests in a browser, open *test/test.html*.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ node toFraction
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Minify
|
||||
|
||||
## Build
|
||||
Two minification examples:
|
||||
|
||||
For Node, if [uglify-js](https://github.com/mishoo/UglifyJS2) is installed
|
||||
Using [uglify-js](https://github.com/mishoo/UglifyJS) to minify the *decimal.js* file:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm install uglify-js -g
|
||||
uglifyjs decimal.js --source-map url=decimal.min.js.map -c -m -o decimal.min.js
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
then
|
||||
Using [terser](https://github.com/terser/terser) to minify the ES module version, *decimal.mjs*:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
npm run build
|
||||
npm install terser -g
|
||||
terser decimal.mjs --source-map url=decimal.min.mjs.map -c -m --toplevel -o decimal.min.mjs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
will create *decimal.min.js*, and a source map will also be added to the *doc* directory.
|
||||
```js
|
||||
import Decimal from './decimal.min.mjs';
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Licence
|
||||
|
||||
MIT.
|
||||
|
||||
See *LICENCE.md*
|
||||
[The MIT Licence (Expat).](LICENCE.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user